| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Saxe-Meiningen" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Duchy of Saxe-Meiningen (1680–1918) Herzogtum Sachsen-Meiningen Free State of Saxe-Meiningen (1918–1920) Freistaat Sachsen-Meiningen | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1680–1920 | |||||||||
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |||||||||
| Anthem: Meiningen Hymn (“Brothers sing with a loud sound of joy...”) | |||||||||
 Saxe-Meiningen within the German Empire Saxe-Meiningen within the German Empire | |||||||||
 Territories of Saxe-Meiningen within the Ernestine duchies after 1826 Territories of Saxe-Meiningen within the Ernestine duchies after 1826 | |||||||||
| Status | State of the Holy Roman Empire, State of the Confederation of the Rhine, State of the German Confederation, State of the North German Confederation, Constituent state of the German Empire | ||||||||
| Capital | Meiningen | ||||||||
| Government | Duchy (1680–1918) Republic (1918–1920) | ||||||||
| Duke | |||||||||
| • 1675–1706 | Bernhard I (first) | ||||||||
| • 1914–1918 | Bernhard III (last) | ||||||||
| Historical era | Early modern period | ||||||||
| • Partitioned from Saxe-Gotha | 1680 | ||||||||
| • Acquired Saxe-Hildburghausen | 1826 | ||||||||
| • German Revolution | 1918 | ||||||||
| • Merged into Thuringia | 1920 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Saxe-Meiningen (/ˌsæks ˈmaɪnɪŋən/ SAKS MY-ning-ən; German: Sachsen-Meiningen [ˌzaksn̩ ˈmaɪnɪŋən]) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine line of the House of Wettin, located in the southwest of the present-day German state of Thuringia.
Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernestine Duchy of Saxe-Gotha among the seven sons of deceased Duke Ernest the Pious, the Saxe-Meiningen line of the House of Wettin lasted until the end of the German monarchies in 1918.
History

House of Wettin
The Wettiner had been the rulers of sizeable holdings in today's states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia since the Middle Ages. In the Leipziger Teilung of 1485, the Wettiner were split into two branches named after their founding princes Albrecht and Ernst (albertinisch and ernestinisch). Thuringia was part of the Ernestine holdings of Kursachsen (the Electorate of Saxony). In 1572, the branches Saxe-Coburg-Eisenach and Saxe-Weimar were established there. The senior line again split in 1641/41 into three duchies, including the Duchy of Saxe-Gotha.
Duke Ernst I who founded this duchy with its seat at Gotha opposed the system of primogeniture. As a result, on his death in 1675 all of his sons inherited part of his holdings and were supposed to rule under the leadership of his oldest son. In practice, this proved very complicated and brought on three settlements in 1679, 1680 and 1681 that established the following princedoms: Saxe-Gotha (Friedrich), Saxe-Coburg (Albrecht), Saxe-Meiningen (Bernhard), Saxe-Eisenberg (Christian), Saxe-Hildburghausen (Ernst) and Saxe-Saalfeld (Johann Ernst).
Duchy of Saxe-Meiningen
Bernhard, Ernst I's third son, received the town of Meiningen as well as several other holdings (Wasungen und Salzungen, Maßfeld und Sand, Herrenbreitungen, Herpf, Stepfershausen, Utendorf, Mehlis and the former Franconian lands of the extinct House of Henneberg, Henneberg).
Bernhard chose the town of Meiningen as his residence and became the first duke of Saxe-Meiningen. From 1682 Duke Bernhard I had the Schloss Elisabethenburg built and in 1690 established a court orchestra (Hofkapelle), in which Johann Ludwig Bach later became the Kapellmeister (1711).
In the reshuffle of Ernestine territories that occurred following the extinction of the Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg line upon the death of Duke Frederick IV in 1825, Duke Bernhard II of Saxe-Meiningen received the lands of the former Duchy of Saxe-Hildburghausen as well as the Saalfeld territory of the former Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld duchy.
As Bernhard II had supported Austria in the 1866 Austro-Prussian War, the prime minister of victorious Prussia, Otto von Bismarck, enforced his abdication in favour of his son George II, after which Saxe-Meiningen was admitted to join the North German Confederation.
By 1910, the duchy had grown to 2,468 km (953 sq mi) and 278,762 inhabitants. The ducal summer residence was at Altenstein Castle. Since 1868, the duchy comprised the Kreise (districts) of Hildburghausen, Sonneberg and Saalfeld as well as the northern exclaves of Camburg and Kranichfeld.
End of the Duchy
In the German Revolution after World War I, Duke Bernhard III, brother-in-law of Emperor Wilhelm II, was forced to abdicate and his brother Ernst on 11/12 November 1918 refused the succession. The succeeding "Free State of Saxe-Meiningen" was merged into the new state of Thuringia on 1 May 1920.
Dukes of Saxe-Meiningen


- Bernhard I (1680–1706)
- Ernst Ludwig I (1706–24), son of Bernhard I
- Ernst Ludwig II (1724–29), son of Ernst Ludwig I
- Karl Friedrich (1729–43), son of Ernst Ludwig I
- Friedrich Wilhelm (1743–46), son of Bernhard I
- Anton Ulrich (1746–63), son of Bernhard I
- Karl Wilhelm (1763–82), son of Anton Ulrich
- George I (1782–1803), son of Anton Ulrich, father of Queen Adelaide
- Bernhard II (1803–66), son of Georg I
- Georg II (1866–1914), son of Bernhard II
- Bernhard III (1914–18), son of George II
Notes:
- Friedrich Wilhelm and Friedrich II of Saxe-Gotha reigned as guardians for the minor Karl Friedrich in 1729–1733
- Friedrich Wilhelm and Anton Ulrich reigned jointly in 1743–46
- Charlotte Amalie reigned as regent/guardian for the minors Karl Wilhelm und Georg I in 1763–82
- Luise Eleonore reigned as regent/guardian for the minor Bernhard II in 1803–1821
- Dukedom abolished in 1918.
See also
References
- Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Saxe-Meiningen" . Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- ^ "Die herzogliche Familie (German)". Meininger Museen. Archived from the original on 18 August 2017. Retrieved 10 May 2019.
External links
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Saxe-Meiningen" . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
| Electorates |  | |
|---|---|---|
| Ecclesiastical | ||
| Secular | ||
| Prelates | ||
| Counts / Lords | ||
| Circles est. 1500: Bavarian, Swabian, Upper Rhenish, Lower Rhenish–Westphalian, Franconian, (Lower) Saxon Circles est. 1512: Austrian, Burgundian, Upper Saxon, Electoral Rhenish · Unencircled territories See also: Ernestine duchies | ||
| Ernestine duchies after the Division of Erfurt (1572) | ||
|---|---|---|
|  | |
| States of the Confederation of the Rhine (1806–1813) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank elevated by Napoleon |
| 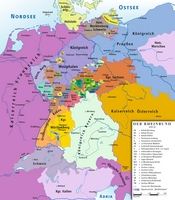 | ||||||
| States created |
| |||||||
| Pre-existing states |
| |||||||
| ||||||||
| States of the German Confederation (1815–1866) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empires | 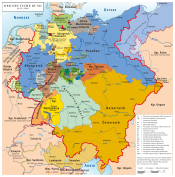 | ||||||||
| Kingdoms | |||||||||
| Electorates | |||||||||
| Grand duchies | |||||||||
| Duchies |
| ||||||||
| Principalities |
| ||||||||
| Free cities | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| States of the North German Confederation (1866–1871) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kingdoms | 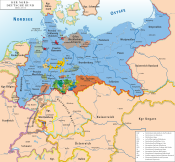 | |
| Grand Duchies | ||
| Duchies | ||
| Principalities | ||
| City-states | ||
| States of the German Empire (1871–1918) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kingdoms |
|  |
| Grand Duchies | ||
| Duchies | ||
| Principalities | ||
| City-states | ||
| Imperial Territories | ||
| Other | ||
Categories:
- States and territories disestablished in 1918
- States of the Confederation of the Rhine
- States of the German Confederation
- States of the North German Confederation
- States of the German Empire
- States of the Weimar Republic
- Ernestine duchies
- Dukes of Saxe-Meiningen
- House of Saxe-Meiningen
- House of Wettin
- South Thuringia
- 1680 establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
- 1918 disestablishments in Germany