In planetary nomenclature, a tholus /ˈθoʊləs/ (pl. tholi /ˈθoʊlaɪ/) is a small domical mountain or hill. The word is from the Greek θόλος, tholos (pl. tholoi), which means a circular building with a conical or vaulted roof. The Romans transliterated the word into the Latin tholus, which means cupola or dome. In 1973, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) adopted tholus as one of a number of official descriptor terms for topographic features on Mars and other planets and satellites. One justification for using neutral Latin or Greek descriptors was that it allowed features to be named and described before their geology or geomorphology could be determined. For example, many tholi appear to be volcanic in origin, but the term does not imply a specific geologic origin. Currently (March 2015), the IAU recognizes 56 descriptor terms. (See Planetary nomenclature.) Tholi are present on Venus, Mars, asteroid 4 Vesta, dwarf planet Ceres, and on Jupiter's moon Io.
-
 Map of the Tharsis quadrangle showing major features, several of which are tholi. Tharsis contains many volcanoes, including Olympus Mons, the tallest known volcano in the Solar System.
Map of the Tharsis quadrangle showing major features, several of which are tholi. Tharsis contains many volcanoes, including Olympus Mons, the tallest known volcano in the Solar System.
-
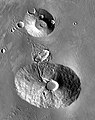 2001 Mars Odyssey THEMIS mosaic of Ceraunius Tholus (lower volcano) and Uranius Tholus (upper volcano). Ceraunius Tholus is about as high as Earth's Mount Everest.
2001 Mars Odyssey THEMIS mosaic of Ceraunius Tholus (lower volcano) and Uranius Tholus (upper volcano). Ceraunius Tholus is about as high as Earth's Mount Everest.
-
 Western part of Jovis Tholus, as seen by THEMIS on Mars Odyssey spacecraft. Jovis Tholus is in the Tharsis quadrangle.
Western part of Jovis Tholus, as seen by THEMIS on Mars Odyssey spacecraft. Jovis Tholus is in the Tharsis quadrangle.
Examples of tholi
References
- ^ "Descriptor Terms (Feature Types)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN). Archived from the original on 2012-05-25. Retrieved 2013-06-24.
- Hargitai H. (2014). "Tholus, Tholi". In H. Hargitai; Á. Kereszturi (eds.). Encyclopedia of Planetary Landforms. Springer New York. p. 1. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-9213-9_371-1. ISBN 978-1-4614-9213-9. Archived from the original on 2015-01-01.
- Liddell & Scott (1889). An Intermediate Greek-English Lexicon. New York: Harper & Brothers. p. 368.
- "Tholus". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Simpson, D.P. (1968). Cassell's New Latin Dictionary; Funk & Wagnalls: New York, p. 604.
- De Vaucouleurs G.; Davies M.; Dollfus A.; Koval I. K.; Masursky H.; Miyamoto S.; et al. (September 1975). "The new Martian nomenclature of the international Astronomical Union" (PDF). Icarus. 26 (1): 85–98. Bibcode:1975Icar...26...85D. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(75)90146-3. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 7, 2014.
- Greeley, R. (1994) Planetary Landscapes, 2nd ed.; Chapman & Hall: New York, pp. 35-36.
- Russell, J.F.; Snyder, C.W.; Kieffer, H.H. (1992). Origin and Use of Martian Nomenclature in Mars, H.H. Kieffer et al., Eds.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, p. 1310.
- Russell, J.F.; Snyder, C.W.; Kieffer, H.H. (1992). Origin and Use of Martian Nomenclature in Mars, H.H. Kieffer et al., Eds.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, p. 1312.
External links
| Geography and geology of Mars | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
This geology article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |