| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Sognamål dialect" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Sognamål dialect | |
|---|---|
| sognamaol | |
| Region | Sogn |
| Language family | Indo-European
|
| Early forms | Old Norse |
| Writing system | Latin (Norwegian alphabet) Norwegian Braille |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| IETF | no-u-sd-no14 |
| This article contains IPA phonetic symbols. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Unicode characters. For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. | |
Sognamål (literally "Sogn language", in Sognamål; sognamaol) is a Western Norwegian dialect which is spoken in the area of Sogn. One of the most prominent features of Sognamål is the pronunciation instead of in many words, i.e. exactly how the letter "á" is pronounced in modern Icelandic. The folk/black metal band Windir from Sogndal used the dialect in their lyrics.
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ||||
| Plosive / Affricate |
voiceless | p | t | c͡ç | k | |
| voiced | b | d | ɟ͡ʝ | ɡ | ||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | s | h | ||
| voiced | v | |||||
| Trill | r | |||||
- /m, p, b/ are bilabial, whereas /f, v/ are labiodental.
- /p, b, t, d, k, ɡ/ are plosives, whereas /c͡ç, ɟ͡ʝ/ are affricates.
- Phonetically, /r/ can be trilled [r] or tapped [ɾ].
Vowels

| Front | Back | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | |||||
| short | long | short | long | short | long | |
| Close | i | iː | ʊ | ʊː | ||
| Mid | ɛ | eː | ø | øː | ɔ | ɔː |
| Open | a | aː | ||||
- /eː/ is close-mid front [eː]. Its short counterpart is the open-mid front [ɛ].
- /ʊ, ʊː/ are close-mid .
- The long /øː/ is open-mid front [œː], whereas the short /ø/ varies between open-mid front [œ] and near-close front [ʉ̞˖].
- /ɔ, ɔː/ are open-mid .
- /a, aː/ are central .
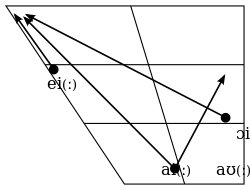

| Starting point | Ending point | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Front | Back | |||||
| unrounded | rounded | |||||
| short | long | short | long | short | long | |
| Close | iʉ | iʉː | ||||
| Close-mid | ei | eiː | eʉ | eʉː | ||
| Open-mid | ɔi | ɔiː | øy | øyː | oʊ | oʊː |
| Open | ai | aiː | aʊ | aʊː | ||
- /iʉ, iʉː/ are phonetically .
- /ei, eiː/ are phonetically .
- /eʉ, eʉː/ are phonetically .
- /øy, øyː/ are phonetically .
- /ɔi, ɔiː/ are phonetically .
- /oʊ, oʊː/ are phonetically .
- /ai, aiː/ are phonetically .
- /aʊ, aʊː/ are phonetically .
References
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (2022-05-24). "Older Runic". Glottolog. Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. Archived from the original on 2022-11-13. Retrieved 2022-11-13.
- ^ Haugen (2004), p. 32.
- ^ Haugen (2004), p. 30.
- Haugen (2004), pp. 30–31.
- ^ Haugen (2004), p. 31.
Bibliography
- Haugen, Ragnhild (2004), Språk og språkhaldningar hjå ungdomar i Sogndal (PDF), Bergen: Universitetet i Bergen
| Norwegian language | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Varieties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other topics | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Institutions | |||||||||||||||||||||
This article about Germanic languages is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |