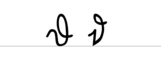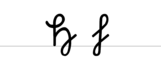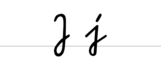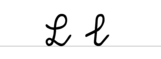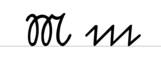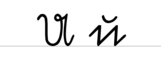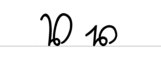This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Latin script (Sütterlin subvariant) | |
|---|---|
 Sample of Sütterlin Sample of Sütterlin | |
| Script type | Alphabet |
| Time period | 1915–1970s |
| Direction | Left-to-right |
| Languages | German |
| Related scripts | |
| Parent systems | Latin script (Blackletter variant)
|
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Latf (217), Latin (Fraktur variant) |
| This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between , / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters. | |
Sütterlinschrift (German pronunciation: [ˈzʏtɐliːnˌʃʁɪft], "Sütterlin script") is the last widely used form of Kurrent, the historical form of German handwriting script that evolved alongside German blackletter (most notably Fraktur) typefaces. Graphic artist Ludwig Sütterlin was commissioned by the Prussian Ministry of Science, Art and Culture (Preußisches Ministerium für Wissenschaft, Kunst und Volksbildung) to create a modern handwriting script in 1911. His handwriting scheme gradually replaced the older cursive scripts that had developed in the 16th century at the same time that letters in books had developed into Fraktur. The name Sütterlin is nowadays often used to refer to several similar varieties of old German handwriting, but Sütterlin's own script was taught only from 1915 to 1941 in all German schools.
History
The ministry had asked for "modern" handwriting scripts to be used in offices and to be taught in school. Sütterlin created two scripts in parallel with the two typefaces that were in use (see Antiqua–Fraktur dispute). The Sütterlin scripts were introduced in Prussia in 1915 and from the 1920s onwards they began to replace the relatively similar old German handwriting (Kurrent) in schools. In 1935 the Sütterlin style officially became the only German script taught in schools.
The Nazi Party banned all "broken" blackletter typefaces in 1941, which were seen as chaotic, including Sütterlin, and replaced them with Latin-type letters such as Antiqua. However many German speakers who had been brought up with that writing system continued to use it well into the postwar period.
Sütterlin continued to be taught in some German schools until the 1970s but no longer as the primary script.
Characteristics
Sütterlin is based on older German handwriting, which is a handwriting form of the Blackletter scripts such as Fraktur and Schwabacher, the German print scripts used at the same time.
It includes the long s (ſ) as well as several standard ligatures such as ff (f-f), ſt (ſ-t), st (s-t), and ß (ſ-z or ſ-s).
Because of their distinctiveness, Sütterlin letters can be used on the blackboard for certain mathematical symbols that are represented by Fraktur letters in print. The lower-case d in Kurrent and Sütterlin is used in proofreading for deleatur ("let it be deleted").
The Sütterlin lower-case 'e' contains two vertical bars close together, in which the origin of the umlaut diacritic (¨) from a small 'e' written above the modified vowel can be seen.
Overview of the letters
(There are two lower-case forms of the letter "s". The second one is used at the end of a syllable.)
A a B b C c D d E e F f G g H h I i J j K k L l M m N n O o P p Q q R r S ſ s ß T t U u V v W w X x Y y Z z Ä ä Ö ö Ü üExamples
-
The text Bäckerei in Sütterlin script in Wismar, northern Germany
-
In Petersberg Citadel, Erfurt: Arreststube Nr. 1 ("lock-up room No. 1"). Notice the long s's.
-
Offizierswache ("officers' guardroom"). Notice the round s at the end of Offiziers, since it occurs at the end of a syllable.
-
Grenadierwache, "grenadiers' guardroom"
-
 Computer font version (text from What is Enlightenment? by Immanuel Kant)
Computer font version (text from What is Enlightenment? by Immanuel Kant)
See also
- Antiqua–Fraktur dispute
- Blackletter
- Eszett (letter ß)
- Fraktur
- Kurrent
- Grundschrift handwriting
Notes
- "Bisweilen wird jede Form der deutschen Kurrentschrift als Sütterlinschrift bezeichnet. Dies liegt wohl daran, daß die Sütterlinschrift diejenige Form der deutschen Kurrentschrift ist, deren Namen am bekanntesten ist. Trotzdem ist diese Bezeichnung unzutreffend, denn es gab die deutsche Kurrentschrift schon lange vor Ludwig Sütterlin."
References
- -donald- (30 September 2008). "Sütterlin.svg". Wikimedia Commons. Retrieved 5 July 2017.
External links
- The Sütterlin script at Omniglot
- German language page about Sütterlin — with history of German cursive handwriting and Sütterlin
- Learn Sütterlin, a lesson, with sample texts
| Types of handwritten European scripts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ancient and medieval |  | |
| Modern | ||
| Teaching scripts | ||