| Transrectal ultrasonography | |
|---|---|
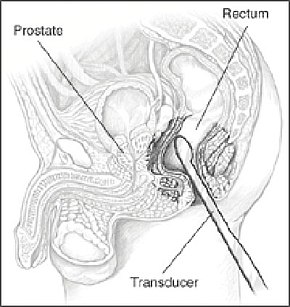 A probe inserted in the rectum emits sound waves to image the prostate A probe inserted in the rectum emits sound waves to image the prostate | |
| ICD-9-CM | 88.74 |
| OPS-301 code | 3-058 |
Transrectal ultrasonography, or TRUS in short, is a method of creating an image of organs in the pelvis, most commonly used to perform an ultrasound-guided needle biopsy evaluation of the prostate gland in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen or prostatic nodules on digital rectal exam. TRUS-guided biopsy may reveal prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia, or prostatitis. TRUS may also detect other diseases of the lower rectum and can be used to stage primary rectal cancer.
References
- O' Donoghue PM, McSweeney SE, Jhaveri K (2010). "Genitourinary imaging: current and emerging applications". J Postgrad Med. 56 (2): 131–9. doi:10.4103/0022-3859.65291. PMID 20622393.
- Shetty, Sugandh (4 August 2016). "Transrectal Ultrasonography of the Prostate". Medscape. Retrieved 18 June 2019.(subscription required)
- Kim, Min Ju (2014-11-19). "Transrectal ultrasonography of anorectal diseases: advantages and disadvantages". Ultrasonography. 34 (1): 19–31. doi:10.14366/usg.14051. ISSN 2288-5919. PMC 4282231. PMID 25492891.
| Tests and procedures involving the human digestive system | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digestive system surgery | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digestive tract |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accessory |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abdominopelvic |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Clinical prediction rules | |||||||||||||||||||||||
This medical diagnostic article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |