| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Numantia" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Numancia | |
 | |
 | |
| Location | Garray (Soria), Spain |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 41°48′34.51″N 2°26′39.33″W / 41.8095861°N 2.4442583°W / 41.8095861; -2.4442583 |
| Type | Archaeological site |
| History | |
| Cultures | Celtiberian |
| Spanish Cultural Heritage | |
| Type | Non-movable |
| Criteria | Archaeological site |
| Designated | 25 August 1882 |
| Reference no. | RI-55-0000001 |
Numantia (Spanish: Numancia) is an ancient Celtiberian settlement, whose remains are located on a hill known as Cerro de la Muela in the current municipality of Garray (Soria), Spain.
Numantia is famous for its role in the Celtiberian Wars. In 153 BC, Numantia experienced its first serious conflict with Rome. After twenty years of hostilities, in 133 BC the Roman Senate gave Scipio Aemilianus Africanus the task of destroying Numantia.
History
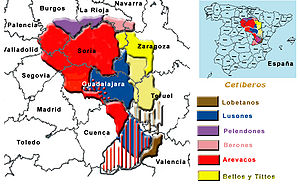
Numantia was an Iron Age hill fort (in Roman terminology an oppidum), which controlled a crossing of the river Duero. Pliny the Elder counts it as a city of the Pellendones, but other authors, like Strabo and Ptolemy place it among the Arevaci people. The Arevaci were a Celtiberian tribe, formed by the mingling of Iberians and migrating Celts in the 6th century BC, who inhabited an area near Numantia and Uxama.
The first serious conflict with Rome occurred in 153 BC when Quintus Fulvius Nobilior was consul. Numantia took in some fugitives from the city of Segeda, who belonged to another Celtiberian tribe called the Belli. The leader of the Belli, Carus of Segeda, managed to defeat a Roman army. The Romans then besieged Numantia, and deployed a small number of war elephants, but were unsuccessful.
In 137 BC, 20,000 Romans surrendered to the Celtiberians of Numantia (population between 4,000 and 8,000). The young Roman officer Tiberius Gracchus, as quaestor, saved the Roman army from destruction by signing a peace treaty with the Numantines, an action generally reserved for a legate.

The final siege of Numantia began in 134 BC. Scipio Aemilianus in command of an army of 30,000 soldiers laid siege to the city, erecting a 9 km barrier supported by towers, moats, impaling rods, and other devices. The Numantians refused to surrender and famine quickly spread through the city. After eight months most of the inhabitants decided to commit suicide rather than become slaves. A few hundred of the inhabitants decided to burn the city before surrendering after 13 months of siege.
Later history

After the destruction in 133 BC, occupation continued in the 1st century BC with a regular street plan but without great public buildings. Its decay started in the 3rd century, but was still settled in the 4th century.
Later remains from the 6th century hint of a Visigoth occupation.
Excavation and conservation of Numantia
Numantia's exact location vanished from memory, and some theories placed it in Zamora, but in 1860 Eduardo Saavedra identified the correct location in Garray, Soria. In 1882, the ruins of Numantia were declared a national monument. In 1905, the German archaeologist Adolf Schulten began a series of excavations which located the Roman camps around the city. In 1999, the Roman camps were included in a zona arqueológica, a category of the Spanish heritage register which did not exist when the hillfort was first protected. Regular excavations are still going on.
Museums

Many objects from the site are on display in the Numantine Museum of Soria (Spanish: Museo Numantino). This museum is also responsible for in situ displays at Numantia.
Other collections which have items from the site include the Romano-Germanic Central Museum, Mainz. (Some objects were taken by Adolf Schulten to Germany).
Symbolism
The Siege of Numantia was recorded by several Roman historians who admired the sense of freedom of the ancient Iberians and acknowledged their fighting skills against the Roman legions.
In Spanish culture
Miguel de Cervantes (author of Don Quijote) wrote a play about the siege, El cerco de Numancia, which stands today as his best-known dramatic work. Antonio Machado references the city in his poetry book Campos de Castilla. The poem is an ode to the countryside and peoples of rural Castile. More recently, Carlos Fuentes wrote a short story about the event, "The Two Numantias", in his collection The Orange Tree.
Several Spanish Navy ships have been named Numancia and a Sorian battalion was named batallón de numantinos. During the Spanish Civil War, the Nationalist Numancia regiment took the town of Azaña in Toledo. To erase the memory of the Republican president Manuel Azaña, they renamed it Numancia de la Sagra.
The Sorian football team is called CD Numancia.
The expression "numantine resistance" is occasionally used to refer to particularly obdurate resistance.
References
- Keay, S., R. Mathisen, H. Sivan. "Places: 246523 (Numantia)". Pleiades. Retrieved April 30, 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Pliny. Natural History.
- Monumento and zona arqueológica are both types of Bien de Interés Cultural
- Delgado, Adrián (25 April 2017). "La Numancia inédita de Adolf Schulten". ABC (in Spanish). Madrid: Vocento. Retrieved 11 November 2018.
- "Numantino". Diccionario de la Real Academia Española (in Spanish) (22nd ed.). Real Academia Española. Archived from the original on 24 March 2007. Retrieved 11 November 2018.
Bibliography
- Rafael Trevino "Rome's Enemies 4: Spanish Armies 218 BC – 19 BC", Osprey Military, Man-at-arms Series 180, 1992, ISBN 0-85045-701-7
External links
- James Grout: 'Numantia,' part of the Encyclopædia Romana
- Photo of a reconstructed Celtiberian house at Numantia
- (in Spanish) Information about the current threat to Numantia accessed September 2008
- (in Spanish) Nuevo Cerco a Numancia
- (in Spanish) * Olga Latorre: Nuane
- Numantia: Archaeology and History, multimedia book edited by José María Luzón and María del Carmen Alonso. Texts by Alfredo Jimeno Martínez. 2018.
- Archaeological sites in Castile and León
- Celtiberian cities and towns
- Roman towns and cities in Spain
- Roman sites in Spain
- Roman conquest of the Iberian Peninsula
- Buildings and structures in the Province of Soria
- Former populated places in Spain
- Destroyed populated places
- Celtic towns
- Hill forts in Spain
- Bien de Interés Cultural landmarks in the Province of Soria
- Ruins in Spain