 One of the first Orion rockets (HAWK at the time) shortly after launch. One of the first Orion rockets (HAWK at the time) shortly after launch. | |
| Function | sounding rocket |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | NASA |
| Country of origin | United States |
| Size | |
| Height | 5.60 m |
| Diameter | 0.35 m |
| Mass |
|
| Stages | 1 |
| Launch history | |
| Launch sites | Wallops, White Sands, Poker Flat, Andoya, Esrange, Barreira do Inferno |
| First stage | |
| Thrust | 7 kN |
| [edit on Wikidata] | |
Orion is the designation of a small American sounding rocket. The Orion has a length of 5.60 meters, a diameter of 0.35 m, a launch weight of 400 kg, a launch thrust of 7 kN and a ceiling of 85 kilometers. The Orion, built by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center's Wallops Flight Facility, is also used as an upper stage of sounding rockets, usually paired with a Terrier missile as the first stage, although Nike, Taurus and VS-30 rockets are also used.
Two Orion versions exist:
- Orion, using a Aerojet M22E8 dual-thrust motor (from the MIM-23A Hawk missile).
- Improved Orion using a Aerojet M112 dual-thrust motor (from the MIM-23B I-Hawk missile).
The sounding rocket is launched from Wallops Flight Facility, White Sands, Poker Flat Rocket Range, Andoya Rocket Range, Esrange and Barreira do Inferno.
Incidents
A lightning storm over the Wallops launch pad on 9 June 1987 ignited a NASA Orion rocket and 2 other sounding rockets. The Orion flew horizontally about 300 feet into the ocean. The sounding rockets rose to around 15,000 feet altitude, then fell about 2 miles from the launch pad. No persons were hurt in the incident.
Gallery
-
 Orion carrying experiments developed by students (June 8, 2006)
Orion carrying experiments developed by students (June 8, 2006)
-
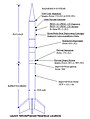 Improved Orion scheme
Improved Orion scheme
-
 Improved Orion just after launch.
Improved Orion just after launch.
-
 Improved Orion launch
Improved Orion launch
References
- International Astronautical Federation; United Nations. Office for Outer Space Affairs; International Institute of Space Law (2007). Highlights in Space 2006: Progress in Space Science, Technology and Applications, International Cooperation and Space Law. United Nations Publications. pp. 58–. ISBN 978-92-1-101147-0.
- ^ Wade, Mark. "Orion Sounding Rocket". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 2013-11-03. Retrieved 2014-05-08.
- "Terrier-Improved Orion (41.XXX)" (PDF).
- Staff, SpaceNews. "NASA Sounding Rocket Tests New Technologies". SpaceNews. Retrieved 2024-04-04.
- ^ "Orion". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 2024-04-05.
- Cowing, Keith (2023-02-18). "NASA Launches Two Sounding Rockets For Tech Research". SpaceRef. Retrieved 2024-04-04.
- Patricia Tanner, Update, Air & Space/Smithsonian, Vol. 2 No. 3 (August/September 1987), p. 21
| Non-military suborbital rocket engines and motors that have flown | ||
|---|---|---|
| Liquid fuel engines |  | |
| Hybrid propellant engines | ||
| Solid propellant motors | ||
| Related articles | ||
This rocketry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |