| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
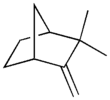
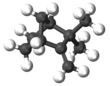
| Preferred IUPAC name 2,2-Dimethyl-3-methylidenebicycloheptane | |||
| Other names
2,2-Dimethyl-3-methanylidenebicycloheptane 2,2-Dimethyl-3-methylenebicycloheptane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.123 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2319 1325 | ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C10H16 | ||
| Molar mass | 136.238 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | White or colorless solid | ||
| Density | 0.842 g/cm | ||
| Melting point | 51 to 52 °C (124 to 126 °F; 324 to 325 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 159 °C (318 °F; 432 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | Practically insoluble | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |   
| ||
| Signal word | Warning | ||
| Hazard statements | H226, H228, H319, H410 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P264, P273, P280, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313, P370+P378, P391, P403+P235, P501 | ||
| Flash point | 40 °C (104 °F; 313 K) | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Camphene is a bicyclic organic compound. It is one of the most pervasive monoterpenes. As with other terpenes, it is insoluble in water, flammable, colorless, and has a pungent smell. It is a minor constituent of many essential oils such as turpentine, cypress oil, camphor oil, citronella oil, neroli, ginger oil, valerian, and mango. It is produced industrially by isomerization of the more common alpha-pinene using a solid acid catalyst such as titanium dioxide.
Camphene is used in the preparation of fragrances and as a food additive for flavoring. These include isobornyl acetate.
Biosynthesis
Camphene is biosynthesized from linalyl pyrophosphate via a sequence of carbocationic intermediates.
References
- IUCLID Datasheet
- Fisher Scientific MSDS
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 1736
- Eggersdorfer, Manfred (2000). "Terpenes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_205. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- Pino, Jorge A.; Mesa, Judith; Muñoz, Yamilie; Martí, M. Pilar; Marbot, Rolando (2005). "Volatile Components from Mango (Mangifera indicaL.) Cultivars". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (6): 2213–2223. doi:10.1021/jf0402633. PMID 15769159.
- Sell, Charles S. (2006). "Terpenoids". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.2005181602120504.a01.pub2. ISBN 0471238961.
- ^ Croteau, R.; Satterwhite, D. M.; Cane, D. E.; Chang, C. C. (1988). "Biosynthesis of Monoterpenes. Enantioselectivity in the Enzymatic Cyclization of (+)- and (-)-Linalyl Pyrophosphate to (+)- and (-)-Pinene and (+)- and (-)-Camphene". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (21): 10063–71. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)81477-1. PMID 3392006.