Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1G subunit, also known as CACNA1G or Cav3.1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CACNA1G gene. It is one of the primary targets in the pharmacology of absence seizure.
Function
Cav3.1 is a type of low-voltage-activated calcium channel, also known as "T-type" for its transient on and off. It is expressed in thalamocortical relay nucleus, and is responsible for the slow-wave sleep and absence seizure. During a slow-wave sleep, Cav3.1 is put into burst mode, and a self-sustaining synchronous cycle between cortex and thalamus is formed, sensory inputs are isolated from cortex; while awake the thalamus should instead relay sensory inputs from outside the central nervous system. The mechanism of absence seizure has a lot in common with slow-wave sleep. Therefore, a blocker that inhibits the burst mode activation of Cav3.1 is effective in treating absence seizures. Common drugs including ethosuximide, as well as trimethadione.
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective Misplaced Pages articles.
[[File: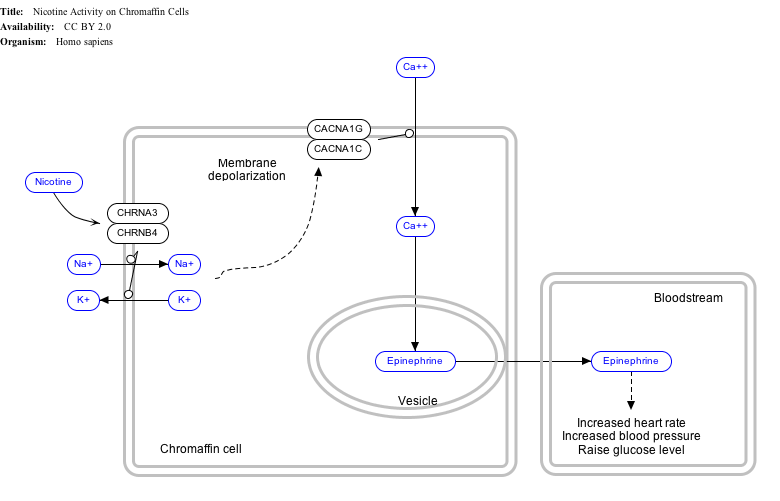

- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "NicotineActivityonChromaffinCells_WP1603".
See also
References
- ^ GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000006283 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020866 – Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: CACNA1H calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1H subunit".
- Perez-Reyes E, Cribbs LL, Daud A, Lacerda AE, Barclay J, Williamson MP, Fox M, Rees M, Lee JH (February 1998). "Molecular characterization of a neuronal low-voltage-activated T-type calcium channel". Nature. 391 (6670): 896–900. Bibcode:1998Natur.391..896P. doi:10.1038/36110. PMID 9495342. S2CID 4373283.
- Catterall WA, Perez-Reyes E, Snutch TP, Striessnig J (December 2005). "International Union of Pharmacology. XLVIII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated calcium channels". Pharmacol. Rev. 57 (4): 411–25. doi:10.1124/pr.57.4.5. PMID 16382099. S2CID 10386627.
- ^ Kopecky, Benjamin J.; Liang, Ruqiang; Bao, Jianxin (2014). "T-type Calcium Channel Blockers as Neuroprotective Agents". Pflügers Archiv. 466 (4): 757–765. doi:10.1007/s00424-014-1454-x. ISSN 0031-6768. PMC 4005039. PMID 24563219.
External links
- CACNA1G+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human CACNA1G genome location and CACNA1G gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
| Membrane transport protein: ion channels (TC 1A) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| see also disorders | |||||||||||||||||
This membrane protein–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |



