
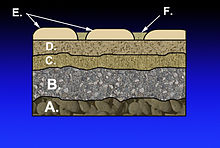
A. Subgrade
B. Subbase
C. Base course
D. Paver base as binder course
E. Pavers as wearing course
F. Fine-grained sand
The base course or basecourse in pavements is a layer of material in an asphalt roadway, race track, riding arena, or sporting field. It is located under the surface layer consisting of the wearing course and sometimes an extra binder course.
If there is a sub-base course, the base course is constructed directly above this layer. Otherwise, it is built directly on top of the subgrade. Typical base course thickness ranges from 100 to 150 millimetres (4 to 6 in) and is governed by underlying layer properties. Generally made of a construction aggregate, it is spread and compacted to at least 95% relative compaction, thus providing a stable foundation for additional layers of material.
Aggregate base (AB) is typically a mix of different sizes of crushed rock 20 mm or 3⁄4 in Aggregate Base, Class 2, is used in roadways and consists of rock particles of size 20 mm (3⁄4 in) and less. An aggregate is normally made from newly quarried rock, or it is sometimes allowed to be made from recycled asphalt concrete and/or Portland cement concrete.
See also
References
- Lay, M. G. (2009). Handbook of Road Technology (4 ed.). Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0203892534.
- Phatak, D. R.; Gite, H. K. Highway Engineering. Nirali Prakashan. ISBN 978-8185790923.