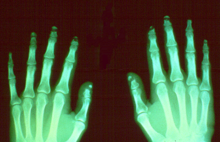
Acroosteolysis is resorption of the distal bony phalanges. Acroosteolysis has two patterns of resorption in adults: diffuse and bandlike.
The diffuse pattern of resorption has a widely diverse differential diagnosis which includes: pyknodysostosis, collagen vascular disease and vasculitis, Raynaud's neuropathy, trauma, epidermolysis bullosa, psoriasis, frostbite, sarcoidosis, hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, acromegaly, and advanced leprosy.
The bandlike pattern of resorption may be seen with polyvinyl chloride exposure and Hadju-Cheney syndrome.
A mnemonic commonly used for acro-osteolysis is PINCHFO. Pyknodysostosis, Psoriasis, Injury (thermal burn, frostbite), Neuropathy (diabetes), Collagen vascular disease (scleroderma, Raynaud's), Hyperparathyroidism, Familial (Hadju-Cheney, progeria), Occupational (polyvinyl exposure),
Acroosteolysis may be associated with minimal skin changes or with ischemic skin lesions that may result in digital necrosis.
See also
References
- ^ Yu, Joseph. Musculoskeletal Imaging, Case Review Series. 2008.
- Romero, Belinchón; Ramos Rincón, J.M.; Reyes Rabellc, F. "Nail Involvement in Leprosy". ACTAS Dermo-Sifiliograficas. Academia Española de Dermatología y Veneralogía. Archived from the original on 28 April 2015. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- Baran, Robert; de Berker, David A. R.; Holzberg, Mark; Thomas, Luc (July 23, 2012). Baran and Dawber's Diseases of the Nails and their Management (4th ed.). Wiley. ISBN 978-0470657355. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- Jones, Jeremy. "Acro-osteolysis (mnemonic) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia. doi:10.53347/rID-12202.
- Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.